Annual Review 2017
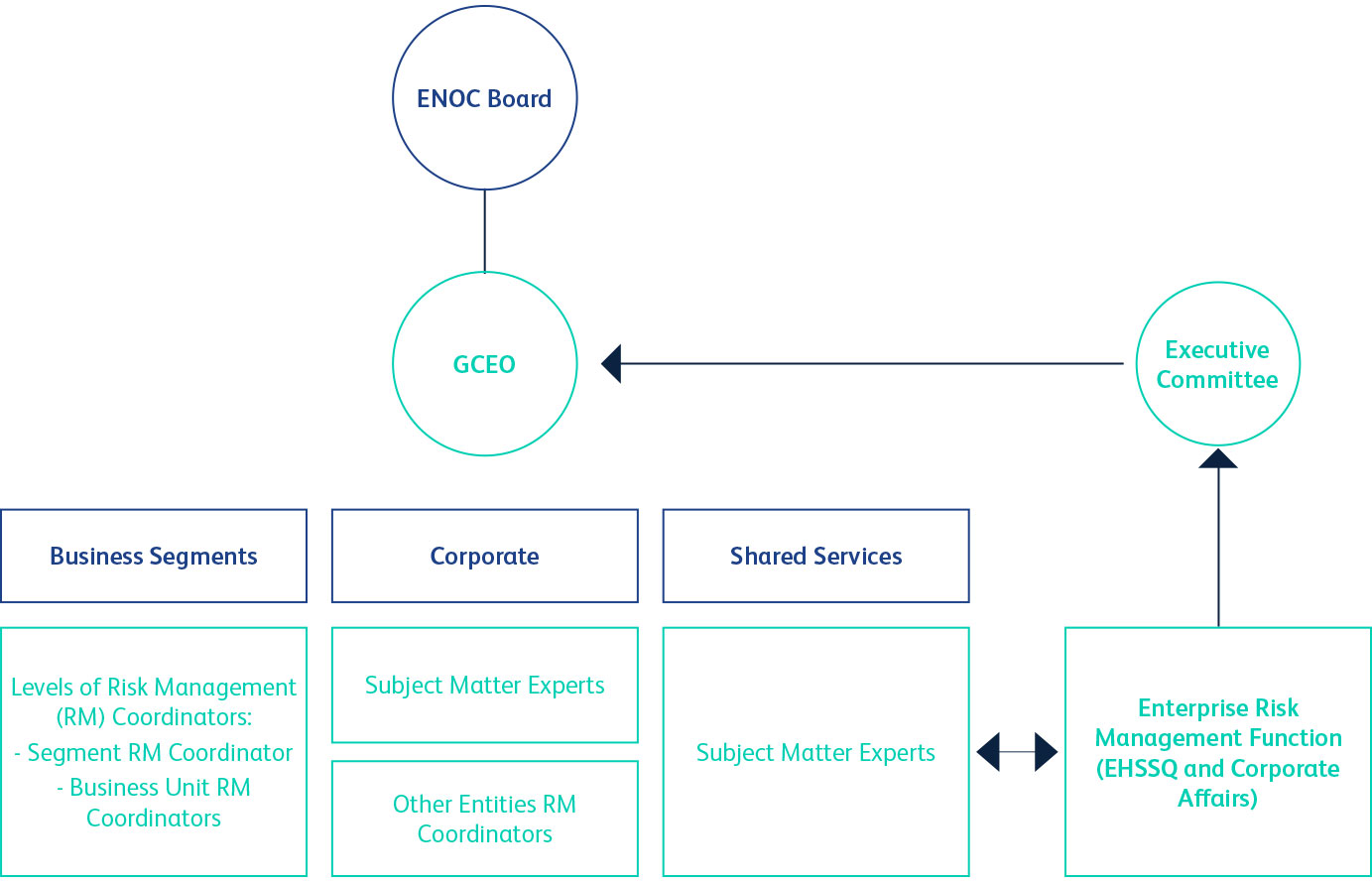
enoc.comENOC Group has adopted an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework that addresses the full spectrum of risks facing our organisation. An integrated, structured, and disciplined approach to risk management ensures that potential risks that may adversely impact our businesses will be appropriately addressed, and that opportunities for growth and development are channelled back into the strategy and objective-setting process.
In view of the dynamic socio-political and economic changes constantly taking place in markets where ENOC Group operates, it is imperative that the organisation continue to follow a cohesive approach to risk management, where resources are channelled to address key strategic, operational, and financial risks in the most effective and efficient manner. Everyone has a role to play in the Group’s ERM – this entails understanding the risks and opportunities facing our businesses, assessing exposure, and acting to effectively respond to preserve and maximise value.
Under the ERM framework, the management team considers ENOC Group’s risk appetite when evaluating strategic alternatives, setting objectives, and developing mechanisms to manage all related risks. The process provides the rigour to identify and select alternative risk responses – risk avoidance, reduction, sharing, and acceptance. The underlying objective is to identify potential events and establish effective responses to interrelated impacts and integrated responses to multiple risks, as well as reduce surprises and the associated costs or losses.
By considering a full range of potential events, the management team is well-positioned to proactively identify opportunities, thereby effectively assessing overall capital needs and enhancing capital allocation.
Within the scope of the ERM framework, the Group has also established a business continuity management programme. In close collaboration with the National Emergency Crisis and Disasters Management Authority (NCEMA) of the UAE Supreme Council for National Security, ENOC Group has achieved key milestones in developing segment-level crisis management plans, establishing a best-in-class crisis management centre and putting in place an emergency response planning management system.
Principal risks
Exploration and Production (E&P)
We recognise that managing risks requires continuous effort. E&P strategy is to embed risk management into the decision-making processes. Its Corporate Risk Register is compiled across the asset portfolio through a top-down and bottom-up review process. Those risks identified as critical and potentially affecting employees, corporate reputation, operations, performance, and assets needed to deliver strategic goals and targets, are identified and recorded through this process.
During the year we review, identify and assess the risks the organisation faces. The principal risks and uncertainties faced by the Group’s E&P operations include:
A prolonged low oil price environment – which can impact the organisation’s development plans, profitability, cash flows, liquidity, and ability to finance planned capital expenditure because of lower revenue, leading to impairment of the organisation’s oil and gas properties, and, consequently, the recoverability of the organisation’s investment in its subsidiaries. The Board intends to retain appropriate levels of cash resources along with optimising short-term business plans.
ENOC’s E&P revenues are dependent on the continued performance of its primary producing asset, the Cheleken Contract Area, offshore Turkmenistan. The Board has adopted a clear strategy for growth and regularly reviews investment opportunities. Dragon Oil has also initiated expansion plans in other countries and production will begin when it is economically viable.
E&P operations must comply with various international and local laws and regulations, including those related to ethical business conduct and international trade. The organisation is therefore implementing a robust and comprehensive corporate compliance programme to identify, assess and mitigate compliance-related risks. Among other things, the programme will cover the areas of ethical business conduct, international trade, third-party due diligence and monitoring, as well as corporate social responsibility.
Supply, Trading and Processing
The primary risk relates to the availability of regular condensate feedstock. Supply and Operations maintains reasonable diversification in sources of supplies for condensate to offset any potential disruption that may arise. Price volatility and counterparty creditworthiness are other key risks facing this segment. Mitigating measures include hedging for exposure, thereby bringing the open position to acceptable level, as well as conducting regular counterparty reviews.
From a processing perspective, key assets are the refinery and the MTBE plant, which significantly contribute to serving the energy needs of Dubai. To ensure the continuity and consistency of effective and efficient refining and processing capacities, these facilities continue to make investments in expansion and undertake adequate protective and safety measures. These include preventive maintenance programmes, updating of resource skillsets through continuous and relevant training, and Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) reviews to mitigate the risks of plant breakdowns and operational disruptions. We conduct regular EHS audits as they are of paramount importance in pre-empting and countering hazards at the processing units and inventory storage locations.
Successful completion of the EPCL Refinery expansion project, due to go online in the latter half of 2019, is also identified as a major risk that could have implications for the entire supply chain.
Adequate strategic and world-class operational policies and procedures are established and adhered to, with continuous compliance monitoring of the Supply and Operations trading, and operational units’ day-to-day functioning.
Terminals
Terminal facilities are impacted by global economic conditions and how those requiring storage facilities react to oil price volatility. Being reliant on product storage requirements that are predominantly determined by industry dynamics such as demand and supply, the segment has addressed risk associated with ensuring that operations run seamlessly in diverse social and political environments.
Concentration within limited markets is also a key risk and is relatively beyond the control of business. However, efforts are made to mitigate this risk by long-term contractual arrangement and provision of various ancillary services that help in retaining customers.
Operations in countries that are susceptible to social and political uncertainties also pose a key threat, and these are mitigated by maintaining a close watch on pertinent developments, as well as constant liaison with authorities.
The risk of product spills and adverse impacts on environment and resultant implication on reputation, business, and profitability are also key risks. These are mitigated with the help of adequate operational controls such as automated systems, periodic infrastructure programmes, regular operational audits, and other EHS measures.
Competition and credit risk are other major risks because of the nature of storage operations. These have self-mitigating aspects such as high barriers of entry, which makes it more difficult for competition to establish facilities. In most contracts, lease payments are taken upfront for the storage period, coupled with the potential lien on the product in the event of non-recoveries.
Marketing
Key marketing risks include competition, price volatility, credit default, and product failure. Mitigating measures to counter competition risk mainly involve efforts to retain market share by providing high-quality service at competitive prices. Where possible, price volatility risk is mitigated by undertaking hedges, while robust credit reviews, regular follow-up, and monitoring ensure that credit exposure is kept to the minimum. Quality checks and prompt resolution of customer issues also result in mitigating the risk of product and service failure.
Marketing activities also include an expanding international business, including supply of jet fuel at 117 airports in 17 countries. Key risks arise from socio-political factors, working culture, and the availability of skilled local workers. Mitigating factors include dialogue with each country’s regulatory authorities, and employee training and development.
The segment’s lubricants manufacturing and blending plants’ risks are associated with infrastructure and EHS. The plants undertake periodic preventive maintenance, operation audit, EHS audits, and employee training to ensure that both plants operate smoothly and safely.
Retail
The Retail segment has a diverse and widely spread range of operations, so the associated risks are also wide-ranging. Key risks identified and adequately mitigated are primarily those associated with retail sites and forecourt operations, where activities range from fuelling vehicles to selling items at convenience stores.
The organisation’s IT infrastructure is critical to the functioning of this segment, as is safeguarding operations against fraud as large volumes of product sales and financial transactions take place every day. To mitigate EHS risks, forecourts are regularly and thoroughly maintained and monitored.
The Retail segment also has a growing network of ENOC petrol stations and ZOOM convenience stores in Saudi Arabia. Like the Marketing segment, key risks arise from socio-political factors, working culture, and the availability of skilled local workers. Mitigating factors include interaction with local regulators and employee training and development.
Risk in the automotive services area is mainly associated with customer satisfaction and efficient turnaround times. The Tasjeel vehicle registration service encounters risk in competition, the financial viability of business collaboration, and non-compliance with policies and procedures. Close monitoring of the business environment through system-based and manual controls ensures these risks are continuously managed.

